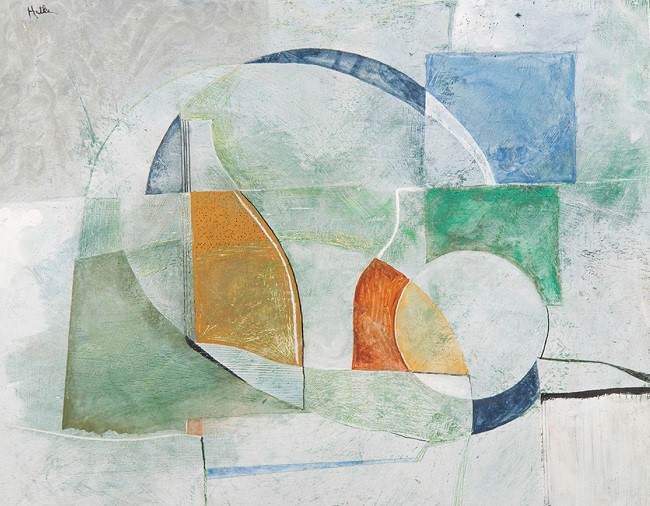Lesson Plan: Shapes
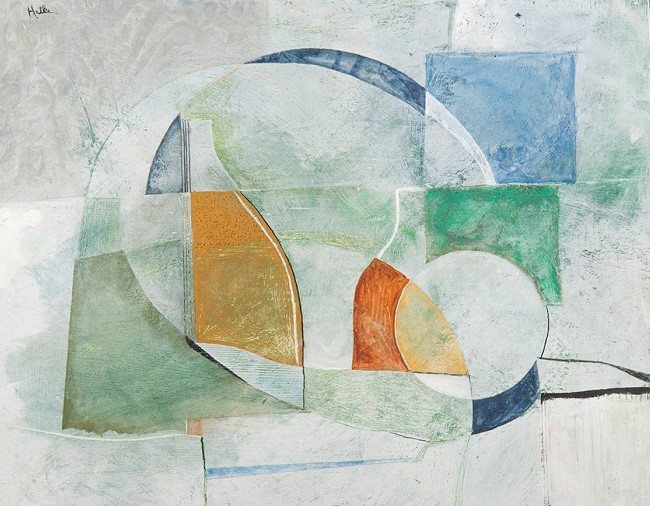
Abstract, Walter Hatke, Acrylic Paint, TSCPL permanent collection
Abstract
Walter Hatke
Acrylic paint, board
TSCPL Permanent Collection
Abstract by Walter Hatke illustrates the use of different types of shapes in creating an artwork. He used hard edged geometric squares and rectangles as well as organic shapes with flowing, natural edges like those in the center of the image.
Emphasis on the two bright orange shapes creates a focal point. He created this effect by adding a varying layer of white over the rest of the composition.
Title
Shapes
Grade
Kindergarten - 5th grade
Media
Paper, Paint
Objectives
- To learn about different types of shapes – organic and geometric
- To learn about emphasis
Vocabulary
- Shape – two-dimensional, flat enclosed area
- Organic shape – natural, found in nature
- Geometric shape - precise edges not found in nature
- Emphasis - focal point where the eye is first drawn
Supplies
- Color paper
- White background paper
- Glue
- Scissors
- White tempera paint (add water to thin like a wash)
- Foam brushes
Resources
Procedure
- Write name on one side. Turn over.
- Cut and tear a few shapes from different colors of paper.
- Arrange on paper to create a pleasing composition. This can be done by dropping one piece at a time onto paper. Rearrange as needed.
- Glue pieces in place.
- Add a layer of thin white paint, chalk or crayon to some areas allowing one area to stand out and the rest to recede.
Reflection
Talk about the artwork:
- How does your artwork make you feel?
- What words can you use to describe your artwork?
- Where do we look first? Is the emphasis clear? Why or why not?
Assessment
- Participants should be able to use art terms.
- Participants should be able to explain how they used shapes to create their composition.
KSDE Visual Art Standards
VA: Cr2.1.K
Through experimentation, build skills in various media and approaches to artmaking.
VA: Cr3.1.2
Discuss and reflect with peers about choices made in creating artwork.
Cross-curricular extensions
Mathematics: Geometry
K.G.2.
Correctly gives most precise name of shapes regardless of their orientations (position and direction in space) or overall size. (K.G.2)
K.G.3.Identify shapes as two-dimensional (lying in a plane, “flat”) or three-dimensional (“solid”). (K.G.3)